Frequently Asked Questions In Cardiology
by Premier Hospitals | January 17, 2020 |
Are you or a loved one interested in learning more about heart health? Regardless of whether you have general questions about heart health or specific questions about Cardiology Services, the FAQ will help you find the answers you are looking for. Below is a list of questions addressed to our FAQ about cardiology provided by Premier Hospital.
How does the heart work usually?
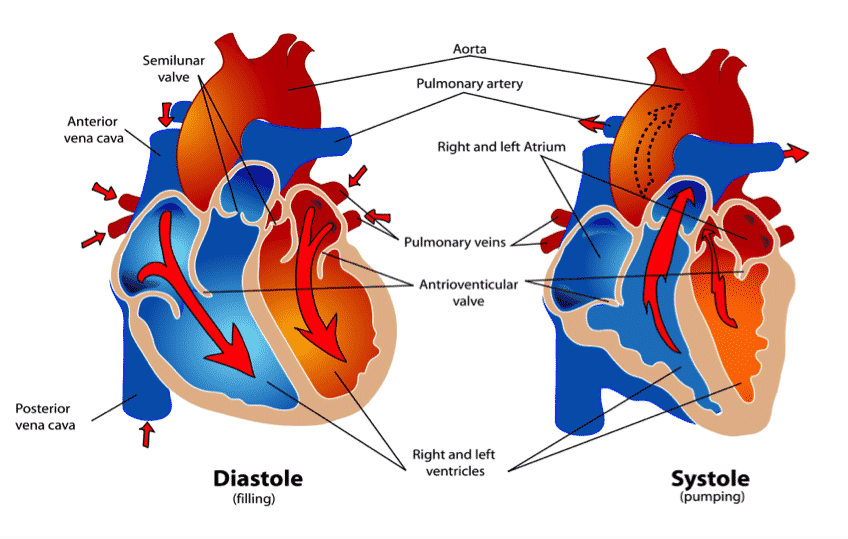 A healthy heart consists of four chambers. The two upper chambers (called the atria) are reservoirs where blood collects when it flows back to the heart. Blood flows from the atrium to the two lower chambers (called the ventricles), which pump blood to the main arteries with each heartbeat. On the right side of the heart, one of these arteries (pulmonary arteries) directs blood to the lungs for oxygenation. The left side of the heart pumps blood to the other main artery (aorta), which leads to blood flow throughout the body.
A septum separates the two ventricles and two atria. The division between the atria is called the "atrial septum" and what divides the ventricular canal is the "ventricular septum". Dark red, oxygen-free blood reaches the right atrium of the body through the two central vein superior vena cava and inferior vena cava. It is pumped from the right ventricle to the lungs for oxygen, and dark blood turns bright red in the lungs when oxygen is absorbed. This red blood returns through two veins from each lung to the left atrium and is pumped back into the body by the left ventricle.
The heart has an internal pacemaker that controls the rhythm. It creates an electrical impulse that starts the atrium, and makes both ventricles to contract. With each contraction, blood gets pumped out, then the heart muscle relaxes, and the space is filled with blood to be ready for the next contraction.
What is a heart attack?
A healthy heart consists of four chambers. The two upper chambers (called the atria) are reservoirs where blood collects when it flows back to the heart. Blood flows from the atrium to the two lower chambers (called the ventricles), which pump blood to the main arteries with each heartbeat. On the right side of the heart, one of these arteries (pulmonary arteries) directs blood to the lungs for oxygenation. The left side of the heart pumps blood to the other main artery (aorta), which leads to blood flow throughout the body.
A septum separates the two ventricles and two atria. The division between the atria is called the "atrial septum" and what divides the ventricular canal is the "ventricular septum". Dark red, oxygen-free blood reaches the right atrium of the body through the two central vein superior vena cava and inferior vena cava. It is pumped from the right ventricle to the lungs for oxygen, and dark blood turns bright red in the lungs when oxygen is absorbed. This red blood returns through two veins from each lung to the left atrium and is pumped back into the body by the left ventricle.
The heart has an internal pacemaker that controls the rhythm. It creates an electrical impulse that starts the atrium, and makes both ventricles to contract. With each contraction, blood gets pumped out, then the heart muscle relaxes, and the space is filled with blood to be ready for the next contraction.
What is a heart attack?
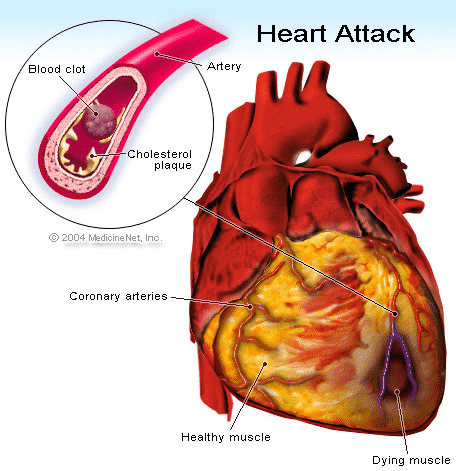 Heart attack refers to the death of heart muscle tissue, which is caused by a sudden blockage of the arteries. It is usually the formation of clots in the buildup of cholesterol called plaque. The most common side effects are chest, arm and neck pain. Current technology allows blocked arteries to be reopened to maintain heart muscle and heart function. It is therefore essential that you visit a doctor immediately after the onset of chest pain and related symptoms.
What are the most common heart attack symptoms?
Heart attack refers to the death of heart muscle tissue, which is caused by a sudden blockage of the arteries. It is usually the formation of clots in the buildup of cholesterol called plaque. The most common side effects are chest, arm and neck pain. Current technology allows blocked arteries to be reopened to maintain heart muscle and heart function. It is therefore essential that you visit a doctor immediately after the onset of chest pain and related symptoms.
What are the most common heart attack symptoms?
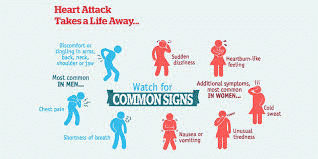 Symptoms of a heart attack include:
Symptoms of a heart attack include:
- Discomfort, pressure, heaviness, or pain in the chest, arms, or under the chest
- Feeling of discomfort that radiates to the back, neck, jaw, or arms
- A feeling of poor digestion or suffocation (may feel acidic)
- Sweating, nausea, vomiting or dizziness
- Extreme weakness, anxiety or shortness of breath
- Irregular heartbeat
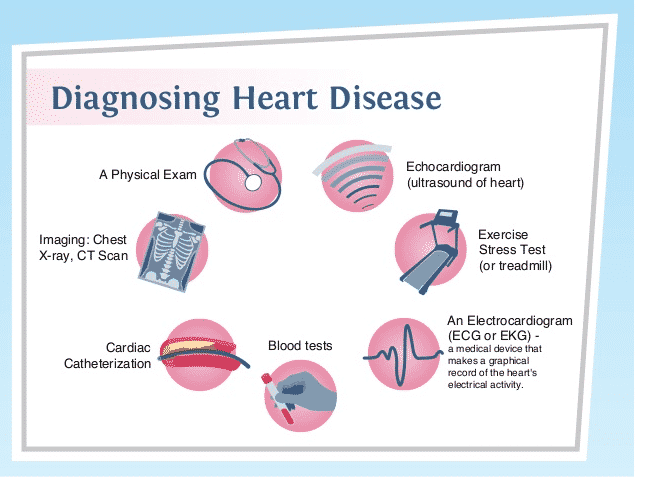 The test that you need, to diagnose your heart condition, depends on your doctor's opinion. Whatever type of heart disease you have, your doctor will most likely do a physical exam and ask about your personal and family health history before conducting the test. In addition to blood tests and chest X-rays, tests to diagnose heart disease can include:
The test that you need, to diagnose your heart condition, depends on your doctor's opinion. Whatever type of heart disease you have, your doctor will most likely do a physical exam and ask about your personal and family health history before conducting the test. In addition to blood tests and chest X-rays, tests to diagnose heart disease can include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Holter monitoring
- Echocardiography
- Stress test
- Cardiac catheterization
- Cardiac computerized tomography (CT) scan
- Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
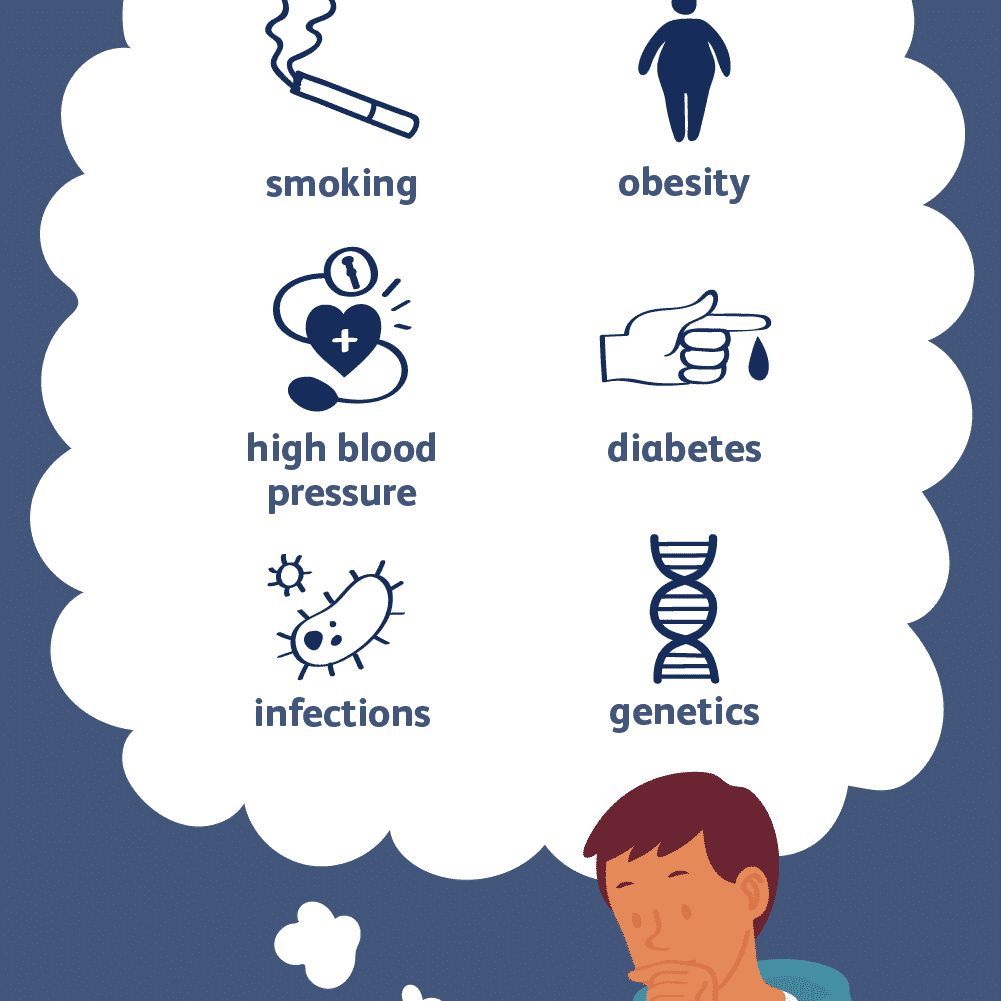 There are several risk factors that you cannot do anything about (non-modifiable). This includes:
There are several risk factors that you cannot do anything about (non-modifiable). This includes:
- Being male
- Being a woman who is past menopause
- Being older
- Having a family history of heart diseases.
- Smoking
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Lack of exercise
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Unhealthy diet
- Stress
- By improving your habits, you can reduce your risk of heart attack or angina.
- Less oxygen supply to the heart
- Higher blood pressure and heart rate
- More blood clotting
- Damage to cells that line coronary arteries and other blood vessels
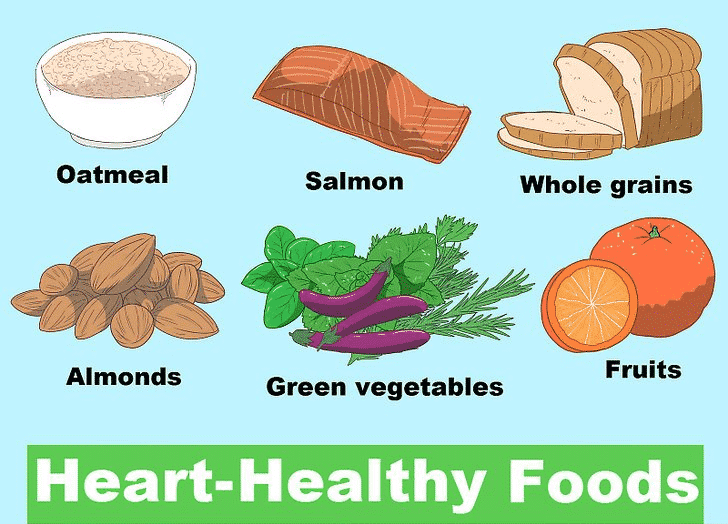 Eating right is an effective way to reduce or even eliminate some risk factors for heart disease. A healthy diet can help you reduce total cholesterol and LDL (bad cholesterol), lower blood pressure, lower blood sugar, and help you lose weight.
Try these tips:
Eating right is an effective way to reduce or even eliminate some risk factors for heart disease. A healthy diet can help you reduce total cholesterol and LDL (bad cholesterol), lower blood pressure, lower blood sugar, and help you lose weight.
Try these tips:
- Eat more vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and nuts.
- Cut fat from your diet. Replace saturated fats with unsaturated fats.
- Eat lean sources of protein such as fish, chicken, and soy. Avoid red meat because it is usually high in fat and cholesterol.
- Eat complex carbohydrates like whole-wheat bread, rice and pasta and limit simple carbohydrates like baking soda, sugar, and cookies.
- Cut salt
- Exercise regularly
- Diabetes
- Smoke
- High blood pressure
- High blood cholesterol, exceptionally high LDL or "bad" cholesterol
- Overweight
- Lack of exercise
- Family history of heart disease
- Pregnancy problems such as pre-eclampsia, high blood pressure, pregnancy diabetes or blood sugar
- Rheumatological and inflammatory diseases
 Cholesterol is a fatty substance in the blood that settles in the arteries and causes progressive obstruction from many different organs, especially the heart. Cholesterol has two components, HDL (right) and LDL (bad). The total number and ratio of these components determine their disposition for the development of plaque in the heart arteries. Triglycerides are another type of fat found in our body, and it increases after a fat-filled meal. It can cause the formation of the lipid molecules which are dangerous for our blood vessels. Lipid profile allows us to take a closer look at all of these components. To understand your fat profile, meet the cardiologist at Premier Hospital.
What is a stroke?
Cholesterol is a fatty substance in the blood that settles in the arteries and causes progressive obstruction from many different organs, especially the heart. Cholesterol has two components, HDL (right) and LDL (bad). The total number and ratio of these components determine their disposition for the development of plaque in the heart arteries. Triglycerides are another type of fat found in our body, and it increases after a fat-filled meal. It can cause the formation of the lipid molecules which are dangerous for our blood vessels. Lipid profile allows us to take a closer look at all of these components. To understand your fat profile, meet the cardiologist at Premier Hospital.
What is a stroke?
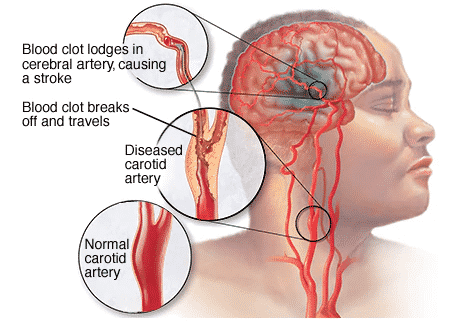 Stroke is the death of brain tissue due to bleeding in the brain or disruption of blood flow to areas of the brain. It can occur at the point of block in the vasculature, or it could be due to passage or embolization of arterial dust particles in the neck, large aorta in the chest, or in the heart itself. It can be a blood clot or cholesterol fragments. Stroke is the most common complication associated with long-lasting and uncontrolled high blood pressure.
Which valve problems affect the heart?
Stroke is the death of brain tissue due to bleeding in the brain or disruption of blood flow to areas of the brain. It can occur at the point of block in the vasculature, or it could be due to passage or embolization of arterial dust particles in the neck, large aorta in the chest, or in the heart itself. It can be a blood clot or cholesterol fragments. Stroke is the most common complication associated with long-lasting and uncontrolled high blood pressure.
Which valve problems affect the heart?
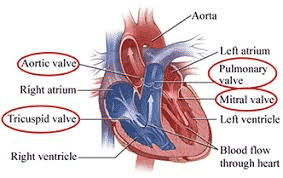 The heart has four valves that control blood flow, two on the right and two on the left. These valves can experience narrowing or stenosis, or it can leak significantly. Abnormalities in heart valves can occur in several ways, including chest pain, leakage, shortness of breath or irregular heartbeat. Diagnostic techniques used for assessment include echocardiography and cardiac catheterization. The mechanical valve can be replaced through surgery if it is critically damaged.
What is arrhythmia?
The heart has four valves that control blood flow, two on the right and two on the left. These valves can experience narrowing or stenosis, or it can leak significantly. Abnormalities in heart valves can occur in several ways, including chest pain, leakage, shortness of breath or irregular heartbeat. Diagnostic techniques used for assessment include echocardiography and cardiac catheterization. The mechanical valve can be replaced through surgery if it is critically damaged.
What is arrhythmia?
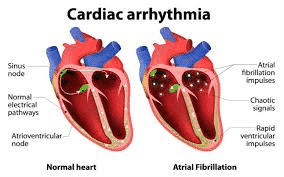 Arrhythmia refers to disorders of the heart rhythm, such as being too slow, too fast or irregular. The most common symptom associated with irregular heartbeats is palpitations or sensations of light-headedness and fainting. The more severe sign is the actual passing out (syncope). During Arrhythmia assessment, It is also essential to determine whether the heart is structurally healthy. How the arrhythmia is treated depends on the condition of the heart's structure and the level of symptoms. Most modern treatments include pacemakers and defibrillators, but medical therapy is often the first line of treatment.
Blood pressure: how high is too high?
Arrhythmia refers to disorders of the heart rhythm, such as being too slow, too fast or irregular. The most common symptom associated with irregular heartbeats is palpitations or sensations of light-headedness and fainting. The more severe sign is the actual passing out (syncope). During Arrhythmia assessment, It is also essential to determine whether the heart is structurally healthy. How the arrhythmia is treated depends on the condition of the heart's structure and the level of symptoms. Most modern treatments include pacemakers and defibrillators, but medical therapy is often the first line of treatment.
Blood pressure: how high is too high?
 There are two numbers associated with blood pressure, the higher (systolic) refers to the peak pressure produced by the contracting heart. The second lower number (diastolic) is the number determined by blood flow to the body with a relaxed heart. Current recommendations assume that these numbers are 130/80 or less. High blood pressure is a leading cause of stroke in the Indian population. Simple things like losing weight and removing sodium from your diet can help in more than 1/3 of cases of healthy blood pressure recovery.
Candidate for heart surgery?
If other treatments such as lifestyle changes, medications, and medical interventions are unsuccessful or cannot be used to treat your heart condition, a heart surgery can be considered. Your doctor, cardiologist and cardiac surgeon will work with you to decide whether heart surgery is the best treatment of choice for you.
Conclusion:
You may feel more tired than usual or out of breath when doing simple tasks like doing household work or going upstairs. Do not ignore such situations. Get yourself checked by a doctor early. Cardiac problems get treated well when you meet the doctor on time.
If you need help or advice, and if you have any questions regarding cardiac health, contact the cardiologist at the premier hospital at +91-77020 01163 or book your appointment now!
There are two numbers associated with blood pressure, the higher (systolic) refers to the peak pressure produced by the contracting heart. The second lower number (diastolic) is the number determined by blood flow to the body with a relaxed heart. Current recommendations assume that these numbers are 130/80 or less. High blood pressure is a leading cause of stroke in the Indian population. Simple things like losing weight and removing sodium from your diet can help in more than 1/3 of cases of healthy blood pressure recovery.
Candidate for heart surgery?
If other treatments such as lifestyle changes, medications, and medical interventions are unsuccessful or cannot be used to treat your heart condition, a heart surgery can be considered. Your doctor, cardiologist and cardiac surgeon will work with you to decide whether heart surgery is the best treatment of choice for you.
Conclusion:
You may feel more tired than usual or out of breath when doing simple tasks like doing household work or going upstairs. Do not ignore such situations. Get yourself checked by a doctor early. Cardiac problems get treated well when you meet the doctor on time.
If you need help or advice, and if you have any questions regarding cardiac health, contact the cardiologist at the premier hospital at +91-77020 01163 or book your appointment now!