Coronary Angioplasty Guide
by Premier Hospitals | July 11, 2021 |
The heart gets blood, nutrients, and oxygen from the coronary arteries so that it can function properly. As plaques build up along the walls of these arteries, they become narrow and hardened, reducing blood flow to the heart. This is referred to as atherosclerosis, and this condition is called coronary artery disease (CAD). Blockages in major arteries can result in chest pain and heart attacks, says our top cardiologist at Premier Hospital. To restore the blood supply to the heart, doctors may suggest coronary angioplasty, a minimally invasive procedure.How Is Coronary Angioplasty and Stent Done?
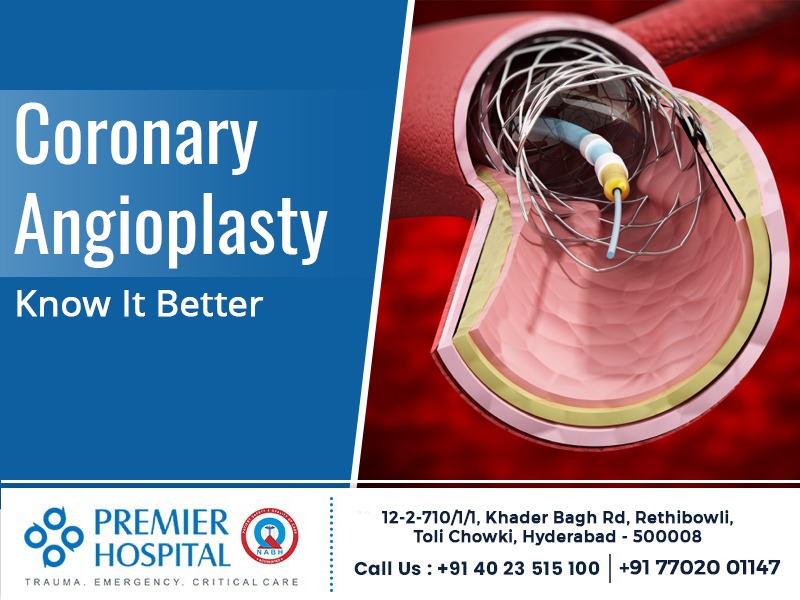
Angioplasty is performed by a cardiologist along with a specialized cardiovascular team in the cardiac catheterization laboratory. It is performed under local anaesthesia, which means you may be awake during the entire procedure. In this procedure, a thin, flexible tube known as a catheter is inserted into an artery located in your groin, wrist, or arm by making an incision. An X-ray video is used to guide the catheter to the affected coronary artery. Once the catheter is in place, a thin wire is guided into the affected artery, and a small balloon is released into the affected area. Then the balloon is inflated, stretching the artery, pushing the plaque against the artery walls to restore blood flow when the deflated balloon is removed. Sometimes, a stent is placed in the blocked area, which is placed around the balloon. After the balloon is inflated, the stent expands and remains in place after the balloon is deflated and removed. Usually, a coronary angioplasty procedure takes anywhere between 30 minutes and 2 hours. Normally, you can return home the same day after your treatment if you're being treated for angina. During the recovery period, you should avoid lifting heavy objects, driving and other strenuous activities for at least a week. If you have been admitted for treatment after a heart attack, you might be under observation in the hospital for some days after the angioplasty procedure.Is a coronary angioplasty safe?
A coronary angioplasty is one of the common treatments for artery blockages that carry blood to the heart. People aged 65 or older are most likely to undergo a coronary angioplasty since they are more likely to suffer from heart disease. Since there are no major incisions to be made in the body, the procedure is typically regarded as extremely safe in most people. So, it is referred to as a minimally invasive surgical treatment. The risk of complications due to Coronary Angioplasty is are and depends on various factors like:- Age
- General health
- Whether having a heart attack or not
- Excessive bleeding
- Heart attack
- Stroke
Is there any alternative procedure?
Your doctor may recommend Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) if your coronary arteries are more narrowed or blocked or if the arteries structure is abnormal. This is an invasive type of surgery that involves removing segments of healthy blood vessels from other body parts and attached to damaged coronary arteries. These vessels divert blood away from narrowed or clogged arteries by bypassing the clogged parts.Why is it done?
Angioplasty is performed to remove fatty plaque that builds up in the walls of the heart's blood vessels. An angioplasty might be a suitable treatment option if:- Medication or lifestyle changes have no effect on improving your heart health.
- You have worsening chest pain (angina).
- If you suffer from a heart attack, then angioplasty is a quick procedure that can open a clogged artery, reducing damage to your heart.
- The artery supplying blood to your left side of the heart becomes narrow
- You have a weak heart muscle
- You have diabetes
- You have multiple blockages in the arteries and
After the procedure
Generally, people might be able to return to their work or daily routine after a week of angioplasty. Drink plenty of fluids when you reach home. Avoid strenuous activities and lifting heavy objects. It's crucial to follow your doctor's post-operative instructions to avoid complications. If you encounter any of the following conditions, consult your doctor immediately:- If bleeding or swelling occurs at the site where the catheter was inserted
- If pain or discomfort develops at the site where the catheter was inserted
- If you observe any signs of infection like redness, swelling, or fever
- If the leg or arm used for the procedure has a change in temperature or colour
- If you feel weak or faint
- If you experience chest pain or shortness of breath
Results
As a result of coronary angioplasty, blood flows much better through the opened arteries. Chest pain decreases, and you can return to regular activities. Stenting and angioplasty don't mean your heart disease will go away. It is extremely crucial to maintain healthy lifestyle habits and take your medications according to the doctor's prescription. Contact your medical professional if you experience chest pain or shortness of breath similar to what you experienced before your surgery. After angioplasty, you should follow the following tips to keep your heart healthy:- Stop smoking
- Take steps to lower your cholesterol
- Eat a healthy, low-fat diet
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Control diabetes and high blood pressure
- Exercise regularly
- Take medications as prescribed by the doctor