COVID-19 Symptoms & Diagnosis | Vital Info
by Premier Hospitals | June 16, 2020 |
The new coronavirus outbreak, first discovered in China in December 2019, continues to affect people throughout the world. Coronavirus (COVID-19) affected all countries around the world. Given that the virus is spreading mainly through close human-to-human contact, the number of cases may increase further in the coming weeks. Early and accurate diagnosis of COVID-19, is very important to limit its spread and improve health outcomes. If you have just been diagnosed with COVID-19, chances are you will have many questions, including "What Next?".
There are many things that we don't know about COVID-19 yet. But we learned a lot in a short time from doctors and researchers and affected patients. More than 30 lakh people worldwide have recovered from the coronavirus. However, the path to full health is not the same for everyone. Recovery time depends on how sick you are. Some people recover quickly, but for others, it can become a permanent problem. Age, sex, and other health problems increase the risk of Covid-19.
Read on to find out what to do if you think you have COVID-19 symptoms and what tests are currently done in India to diagnose the disease and what is the recovery time for Coronavirus disease.
If you have been exposed to a virus or have mild symptoms of COVID-19, contact a doctor for advice on how and when to test. Don't go to your doctor's office personally because you can be contagious. Let's see symptoms of COVID-19 first.
Symptoms of COVID-19:
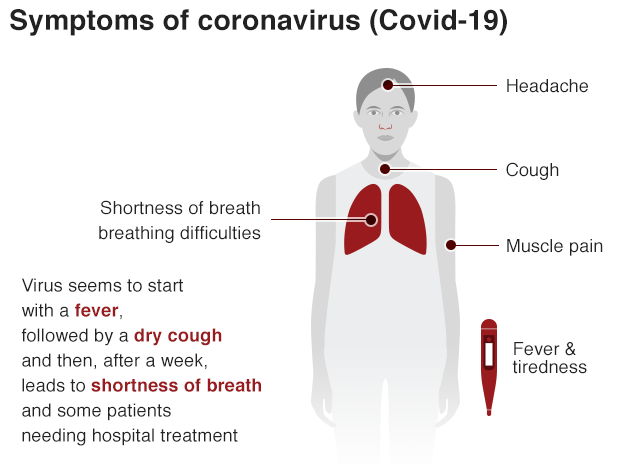 Those infected with COVID-19 sometimes have no symptoms. You might not know that you have COVID-19 symptoms. But others experience symptoms similar to the common cold. The symptoms are:
Those infected with COVID-19 sometimes have no symptoms. You might not know that you have COVID-19 symptoms. But others experience symptoms similar to the common cold. The symptoms are:
- Cough
- Fever
- Hard to breath
- Pneumonia in both lungs
- Haven't developed any symptoms (without symptoms)
- Never develop symptoms (asymptomatic)
 There are two types of COVID-19 tests available:
There are two types of COVID-19 tests available:
- Viral tests: Viral tests indicate whether there is an infection.
- Antibody tests: The antibody test shows whether you previously had an infection.
 About 80% of people infected with new coronavirus have mild symptoms or have no symptoms at all. Someone with mild symptoms can expect to recover within ten days or a week. Information from the World Health Organization (WHO) shows that recovery takes an average of one to two weeks.
If you have a mild illness, you should expect the recovery process to resemble other significant viral respiratory infections, like the flu. People with mild symptoms can recover well and quickly.
Recovery from moderate COVID-19 disease:
The recovery process takes longer in people with more acute or moderate COVID-19 symptoms. In some cases, they will require an ER visit or even hospitalization.
While recovering from a moderate case of COVID-19, you may experience fatigue, coughing, and even breathing difficulties, and these persistent symptoms can last for several weeks. This disease can be much more severe for some people and tends to occur about seven to 10 days after infection.
Transformations can occur suddenly. Breathing becomes difficult, and the lungs are inflamed since the immune system tries to fight a lot, and the body suffers collateral damage. Some people need oxygen therapy at the hospital. Researchers say that it takes two to eight weeks to recover from fatigue.
Recovery from a severe illness COVID-19
About 80% of people infected with new coronavirus have mild symptoms or have no symptoms at all. Someone with mild symptoms can expect to recover within ten days or a week. Information from the World Health Organization (WHO) shows that recovery takes an average of one to two weeks.
If you have a mild illness, you should expect the recovery process to resemble other significant viral respiratory infections, like the flu. People with mild symptoms can recover well and quickly.
Recovery from moderate COVID-19 disease:
The recovery process takes longer in people with more acute or moderate COVID-19 symptoms. In some cases, they will require an ER visit or even hospitalization.
While recovering from a moderate case of COVID-19, you may experience fatigue, coughing, and even breathing difficulties, and these persistent symptoms can last for several weeks. This disease can be much more severe for some people and tends to occur about seven to 10 days after infection.
Transformations can occur suddenly. Breathing becomes difficult, and the lungs are inflamed since the immune system tries to fight a lot, and the body suffers collateral damage. Some people need oxygen therapy at the hospital. Researchers say that it takes two to eight weeks to recover from fatigue.
Recovery from a severe illness COVID-19
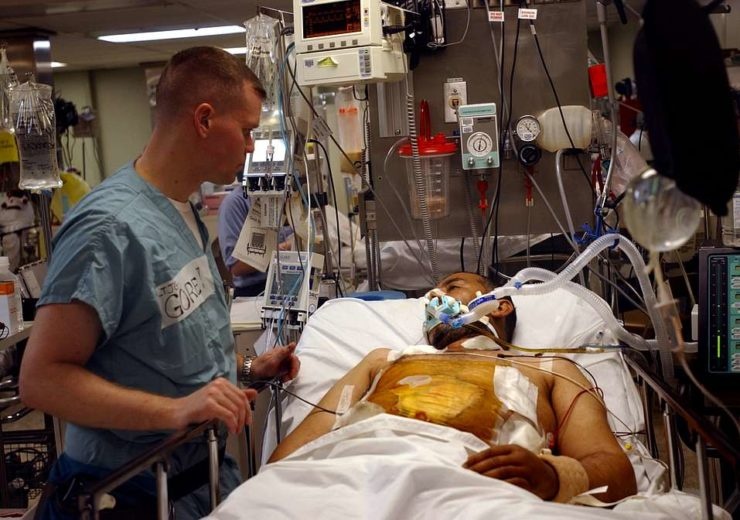 It can take weeks or months for you to recover from a severe COVID-19 disease. You might be in an intensive care unit and might even require a ventilator.
This disease becomes more severe in some people when pneumonia develops, or the immune system triggers a very strong "cytokine storm" to get rid of the virus. This strong inflammatory reaction causes what is called Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), which causes lung tissue damage and maybe even respiratory failure.
Recovery from a severe case of COVID-19 may take time. If you need a ventilator, it will take time for you to regain your independence when you get home. How much time depends only on how much energy you lost and how much damage occurred to the lungs. The patient is taken to an ordinary ward before returning home. It takes 12 to 18 months for you to return to normal after intensive care.
Staying long in a hospital bed causes loss of muscle mass. The patients will be weak and will need time for the muscles rebuilding. Some people need physical therapy to be able to walk again.
There may be long-term side effects from COVID-19:
It can take weeks or months for you to recover from a severe COVID-19 disease. You might be in an intensive care unit and might even require a ventilator.
This disease becomes more severe in some people when pneumonia develops, or the immune system triggers a very strong "cytokine storm" to get rid of the virus. This strong inflammatory reaction causes what is called Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), which causes lung tissue damage and maybe even respiratory failure.
Recovery from a severe case of COVID-19 may take time. If you need a ventilator, it will take time for you to regain your independence when you get home. How much time depends only on how much energy you lost and how much damage occurred to the lungs. The patient is taken to an ordinary ward before returning home. It takes 12 to 18 months for you to return to normal after intensive care.
Staying long in a hospital bed causes loss of muscle mass. The patients will be weak and will need time for the muscles rebuilding. Some people need physical therapy to be able to walk again.
There may be long-term side effects from COVID-19:
 People who went through severe COVID-19 can experience long-term lung damage. There is also evidence that some people tend to develop Cardiomyopathy (A heart muscle disease that makes it difficult for the heart to pump blood throughout the body). Cardiomyopathy can cause heart failure a few weeks after recovery from COVID-19. This is one of the biggest things to worry about people who seem to have recovered fully.
Conclusion:
If you have mild symptoms or suspect an infection, call your doctor. They review your risks, make prevention and treatment plans for you, and give you instructions on what to do next. It is better to be safe than being sorry, so, follow all the preventive measures.
If you need more information about diagnosis and recovery, contact Premier hospital at +91-77020 01163 and book your appointment now!
People who went through severe COVID-19 can experience long-term lung damage. There is also evidence that some people tend to develop Cardiomyopathy (A heart muscle disease that makes it difficult for the heart to pump blood throughout the body). Cardiomyopathy can cause heart failure a few weeks after recovery from COVID-19. This is one of the biggest things to worry about people who seem to have recovered fully.
Conclusion:
If you have mild symptoms or suspect an infection, call your doctor. They review your risks, make prevention and treatment plans for you, and give you instructions on what to do next. It is better to be safe than being sorry, so, follow all the preventive measures.
If you need more information about diagnosis and recovery, contact Premier hospital at +91-77020 01163 and book your appointment now!





