Traumatic Brain Injury: An Overview
by Premier Hospitals | March 2, 2020 |
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a sudden brain injury caused by a blow or a jolt to the head. TBI is a severe public health problem in India. Every year, 3.5 lakh people are killed and many more left with permanent disability in India due to TBI. Common causes are car or motorcycle accidents, falls, sports injuries and physical assaults. Injuries can range from mild to severe, often causing permanent brain damage. While the treatment of mild TBI can include rest and conservative management, severe TBI may require intensive care and life-saving surgeries. Those who experience brain trauma can have a lasting impact on their physical and mental abilities as well as on emotions and personality. Most people with moderate to severe TBI need rehabilitation to recover and re-learn skills. Doctors use neurological exams and imaging techniques to assess TBI. A severe brain injury requires immediate treatment. Treatment and results depend on how severe the damage is. TBI can also be associated with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). This blog provided by Premier Hospital gives general information about Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI). What Is Traumatic Brain Injury?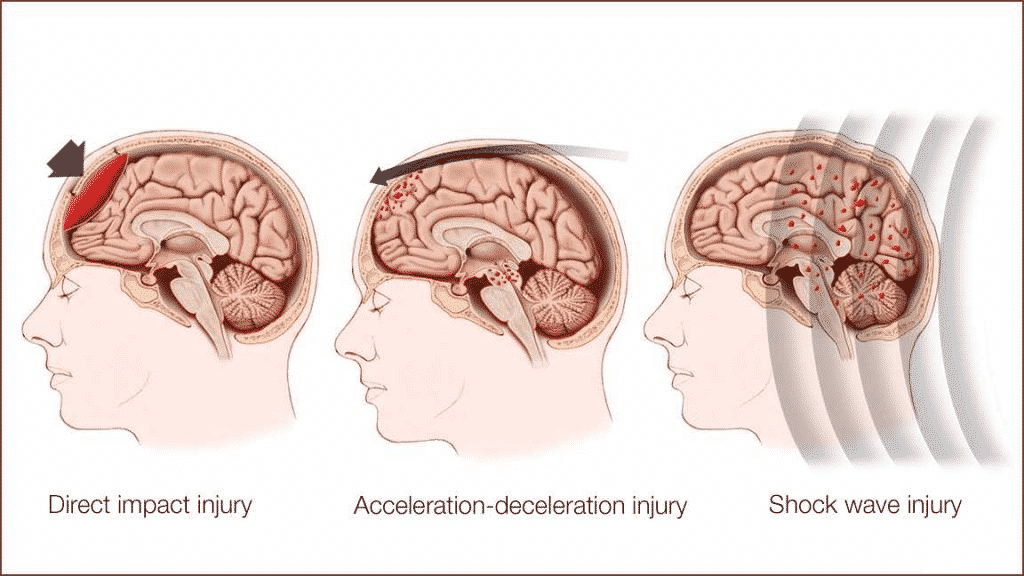 TBI is a brain injury caused by a blow or a jolt to the head due to blunt or penetrating trauma. Injuries that occur during a collision (due to its impact) are called primary injuries. These injuries can involve the whole brain or affect only certain parts of it. During the events of the incident, the brain is thrown back and forth in the skull, causing bruising, bleeding, and nerve fibre tearing. Sometimes, even the bone can fracture, if the impact is forceful enough.
Immediately after the incident, a person may be confused, unable to remember what happened, have blurred and dizzy vision, or loss of consciousness. At first glance, a person may look good, but his condition can deteriorate quickly. After the impact occurs, the brain experiences delayed trauma, swelling that presses on the skull and reduces oxygenated blood flow. It is known as secondary injury, which is often more dangerous than the primary injury. According to severity and mechanism of injury, TBI is classified in to:
TBI is a brain injury caused by a blow or a jolt to the head due to blunt or penetrating trauma. Injuries that occur during a collision (due to its impact) are called primary injuries. These injuries can involve the whole brain or affect only certain parts of it. During the events of the incident, the brain is thrown back and forth in the skull, causing bruising, bleeding, and nerve fibre tearing. Sometimes, even the bone can fracture, if the impact is forceful enough.
Immediately after the incident, a person may be confused, unable to remember what happened, have blurred and dizzy vision, or loss of consciousness. At first glance, a person may look good, but his condition can deteriorate quickly. After the impact occurs, the brain experiences delayed trauma, swelling that presses on the skull and reduces oxygenated blood flow. It is known as secondary injury, which is often more dangerous than the primary injury. According to severity and mechanism of injury, TBI is classified in to:
- Mild: Person will be awake and responsive. Symptoms can include confusion, disorientation, memory loss, headaches and short-term loss of consciousness.
- Moderate: lethargic people; open eyes only on stimulation. They may have swelling or bleeding in the brain that causes drowsiness but are still arousable.
- Severe: a person becomes unconscious. Do not open eyes even on painful stimulation.
- A concussion is a mild head injury that can temporarily cause unconsciousness and generally does not cause permanent brain damage.
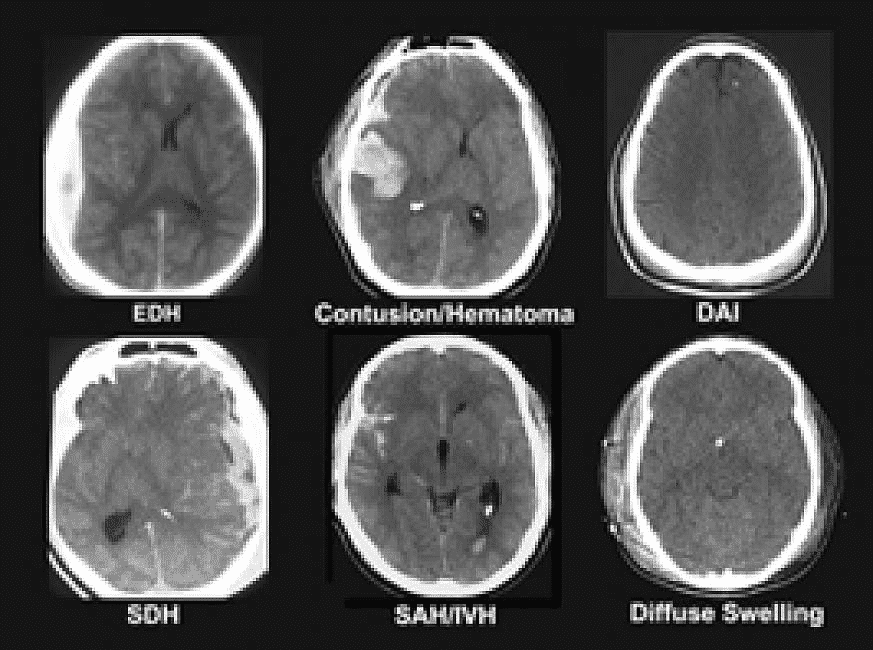
- A contusion is a bruise in a specific area of ​​the brain caused by a blow to the head also called coup or contrecoup injuries. A coup injury is one where the brain gets injured directly under the impact zone and in case of contrecoup injuries on the opposite side of the impact.
- Diffuse axonal injury (DAI) is the shearing and stretching of nerve fibres (axons) at the cellular level. It occurs when the brain quickly moves back and forth inside the skull, tearing and damaging nerve axons. Axons connect one nerve cell to another throughout the brain like a telephone cord. Common axonal injuries interfere with the standard transmission of information to the brain and can cause significant changes in a person's alertness.
- Traumatic subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) bleeds into the space surrounding the brain. This space is usually filled with cerebrospinal fluid, which functions as a floating cushion to protect the brain.
- A hematoma is a blood clot that forms when blood vessels rupture. Blood that comes out of the healthy bloodstream begins to thicken and clot. Blood clots are a natural way for the body to stop bleeding. Hematomas can be small or can grow and compress the brain. Clots that form between the skull and healthy meninges are called epidural hematomas. Clots that form between the brain and the dura are called subdural hematomas. Clots that form deep in brain tissue are called intracerebral hematomas. If the clot is compressing the brain, surgery is done to remove it.
 Depending on the type and location of the injury, the following symptoms may appear:
Depending on the type and location of the injury, the following symptoms may appear:
- Loss of consciousness
- Confusion and disorientation
- Memory loss / amnesia
- Weakness of one side of the body/ limbs
- Headaches
- Visual problems
- Poor attention / concentration
- Sleep disturbances
- Dizziness/loss of balance
- Irritability / emotional disturbances
- Feelings of depression
- Seizures
- Vomiting
 The doctor evaluates the patient's medical history, symptoms, physical examination, and additional tests, including neuroradiology like CT Scan, MRI, to confirm the diagnosis of TBI.
Based on the findings, the doctor then decides on the treatment that is needed. The audiologist will do the test if you have hearing or balance problems. Doctors also test your language, speaking, and thinking skills. They can also see how well you are able to eat and swallow.
Treatment for Traumatic Brain injury:
The doctor evaluates the patient's medical history, symptoms, physical examination, and additional tests, including neuroradiology like CT Scan, MRI, to confirm the diagnosis of TBI.
Based on the findings, the doctor then decides on the treatment that is needed. The audiologist will do the test if you have hearing or balance problems. Doctors also test your language, speaking, and thinking skills. They can also see how well you are able to eat and swallow.
Treatment for Traumatic Brain injury:
 In mild cases of TBI, symptoms usually disappear with minimal treatment. Mild recurrent TBI can be dangerous or fatal. Therefore, you need to rest until the doctor suggests and avoid further trauma. More severe cases require hospitalization, perhaps with intensive care.
Emergency care for severe TBI aims to stabilize the patient's condition and prevent worsening brain damage. It includes opening airways, ventilation and oxygenation, and maintaining blood pressure.
Doctors may use some of the following medications to alleviate symptoms:
In mild cases of TBI, symptoms usually disappear with minimal treatment. Mild recurrent TBI can be dangerous or fatal. Therefore, you need to rest until the doctor suggests and avoid further trauma. More severe cases require hospitalization, perhaps with intensive care.
Emergency care for severe TBI aims to stabilize the patient's condition and prevent worsening brain damage. It includes opening airways, ventilation and oxygenation, and maintaining blood pressure.
Doctors may use some of the following medications to alleviate symptoms:
- Sedation: This can help prevent excessive activity and reduce pain.
- Pain relief: Opioids may be used
- Diuretics: They increase urine output and reduce the amount of fluid in the tissue. They are given intravenously. Mannitol is the most common diuretic used in TBI patients.
- Anti-seizure medication: A person with moderate to severe TBI can experience seizures up to a week after the event. Medications can help prevent further brain damage that can be the result of seizures.
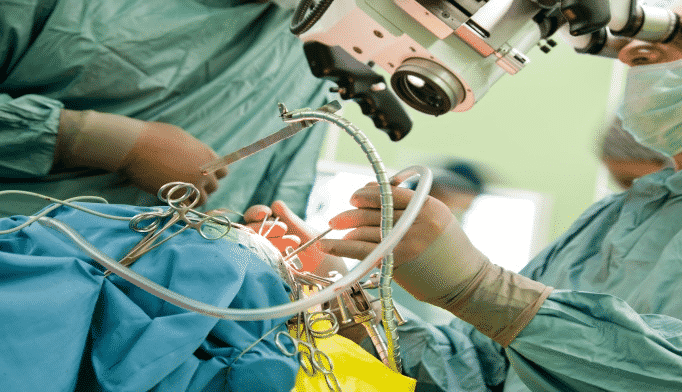
- Removing a hematoma: Internal bleeding can cause partial or complete blood clots in several parts of the brain, increasing pressure on brain tissue. Emergency surgery can remove the hematoma between the skull and brain, reduce pressure on the brain, and prevent further brain damage.
- Repairing a skull fracture: Every part of the skull that is broken and displaced needs to be repaired surgically. Broken skull bones that are not displaced into the brain cavity usually heal by themselves. The main concern with a skull fracture is that, the force that is strong enough to cause a fracture, may have done more damage than is obvious.